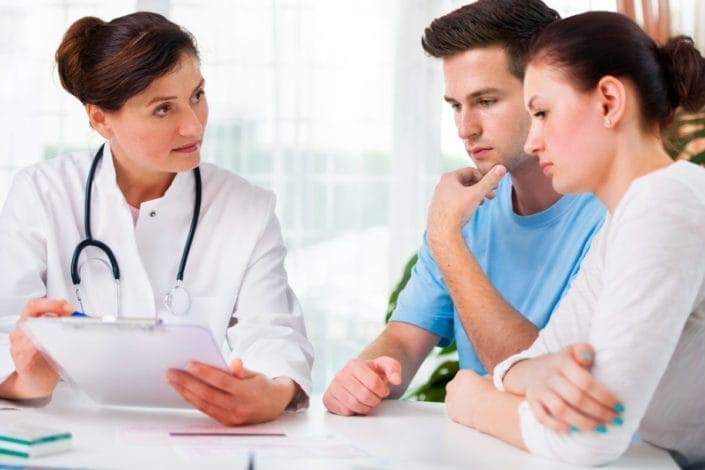
Infertility is a growing concern for many couples worldwide, affecting approximately 15% of couples of reproductive age. It can be a source of immense emotional and psychological stress. Understanding the common causes of infertility and knowing when to seek professional help are essential steps in managing this condition effectively.
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse for women under 35 and after 6 months for women over 35. It can result from factors affecting either partner or a combination of both. In some cases, the cause remains unexplained, known as unexplained infertility, which accounts for about 10-20% of cases.
Common Causes of Infertility in Women
Several factors can contribute to infertility in women, ranging from hormonal imbalances to structural abnormalities and lifestyle factors. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Ovulatory Disorders
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility, affecting up to 10% of women of reproductive age. It is characterized by hormonal imbalances that disrupt ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles or anovulation (absence of ovulation).
- Hypothalamic Dysfunction: The hypothalamus regulates the release of hormones necessary for ovulation. Factors such as excessive stress, low body weight, or high body weight can disrupt its function, leading to irregular ovulation.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): POI, also known as premature ovarian failure, occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop functioning before age 40. This condition can be caused by genetic factors, autoimmune diseases, or cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation.
- Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): PID, often caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea, can cause scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes, preventing the egg and sperm from meeting.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside it, often affecting the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and pelvic tissue. Endometriosis can cause inflammation, scarring, and blockages, hindering conception.
- Previous Surgeries: Surgeries in the pelvic area or for ectopic pregnancies can lead to scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes.
- Uterine or Cervical Issues
- Fibroids and Polyps: These benign growths in the uterus can interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg or block the fallopian tubes, causing infertility.
- Congenital Uterine Abnormalities: Some women are born with uterine malformations that can affect pregnancy outcomes. Examples include a septate uterus or a bicornuate uterus.
- Cervical Mucus Abnormalities: Abnormalities in cervical mucus, often caused by hormonal imbalances or infections, can prevent sperm from traveling through the cervix and reaching the egg.
- Age-Related Infertility
- As women age, their fertility naturally declines. Women over 35 are at a higher risk of infertility due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs. The risk of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities also increases with age.
Common Causes of Infertility in Men
Male infertility can result from various factors, affecting sperm production, function, or delivery. Here are the most common causes:
- Sperm Production Disorders
- Varicocele: A varicocele is a swelling of the veins that drain the testicle, leading to decreased sperm quality and quantity. It is one of the most common reversible causes of male infertility.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormones produced by the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and testicles are crucial for sperm production. Imbalances in these hormones, often due to medical conditions such as hypogonadism, can impair sperm production.
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome (where a man is born with an extra X chromosome) can affect testicular development and sperm production.
- Infections: Infections like mumps, gonorrhea, or chlamydia can cause scarring and blockages in the male reproductive tract, affecting sperm production and delivery.
- Sperm Transport Disorders
- Ejaculatory Disorders: Conditions such as retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during ejaculation, can lead to infertility.
- Blockages: Obstructions in the reproductive tract due to infections, surgeries, or congenital conditions can prevent sperm from being released.
- Lifestyle Factors and Environmental Exposures
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake have been linked to reduced sperm quality and count.
- Drug Use: Anabolic steroids, recreational drugs, and certain medications can negatively impact sperm production.
- Exposure to Toxins: Prolonged exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and chemicals, can affect sperm quality and fertility.
- Medical Conditions and Treatments
- Cancer and Treatments: Chemotherapy, radiation, and surgeries for cancer can impair sperm production or lead to infertility.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, celiac disease, and certain autoimmune disorders can impact male fertility.
When to Seek Help for Infertility
Knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial in addressing infertility issues effectively. Here are some guidelines:
- Women Under 35: If you have been trying to conceive for 12 months without success, it’s advisable to consult a fertility specialist.
- Women Over 35: If you have been trying to conceive for six months without success, you should seek medical advice sooner due to the natural decline in fertility with age.
- Women with Known Risk Factors: If you have irregular menstrual cycles, a history of pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous miscarriages, consider seeking help sooner.
- Men with Known Risk Factors: If you have a history of testicular trauma, varicocele, infections, or surgeries, or if you have difficulty with ejaculation, consult a specialist.
- Couples with Repeated Miscarriages: Recurrent pregnancy loss may indicate an underlying issue that needs medical evaluation.
Diagnostic Tests for Infertility
When you visit a fertility specialist, several diagnostic tests may be recommended to identify the cause of infertility. These tests can include:
- For Women: Ovulation testing, hormone testing, pelvic ultrasound, hysterosalpingography (an X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes), and laparoscopy.
- For Men: Semen analysis, hormone testing, genetic testing, testicular biopsy, and imaging studies like ultrasound.
Infertility can be a challenging and emotional journey, but understanding the common causes and knowing when to seek help can empower couples to take proactive steps. With the advancements in medical science, many treatments and options are available to assist couples in achieving their dream of parenthood. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to improving the chances of a successful pregnancy.