By Saurav Kasera, Co – Founder at Clirnet
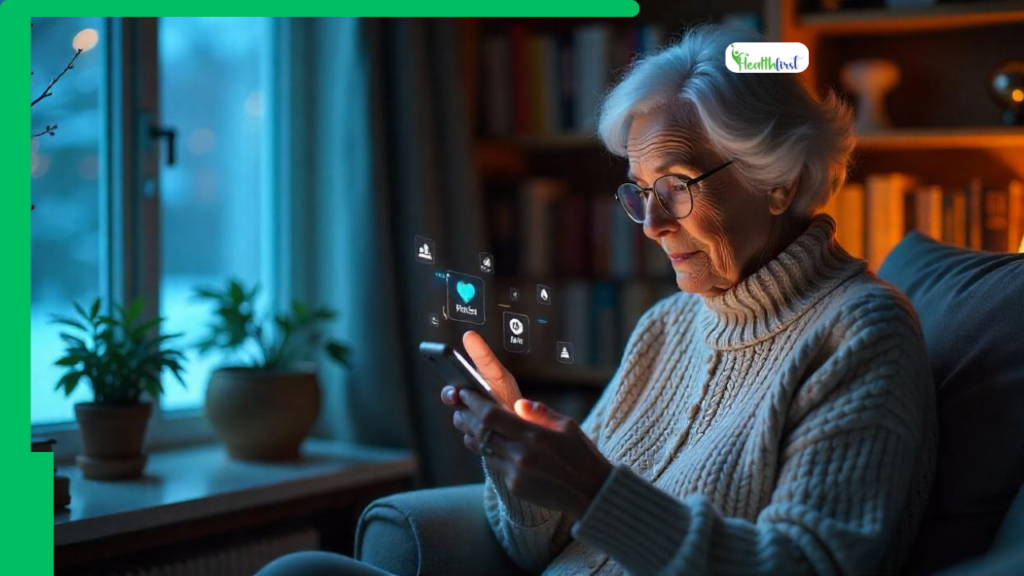
Technological evolution has transformed the healthcare system significantly. Its impact can be felt beyond the boundaries of hospitals and clinics. Previously, home healthcare was mostly attributed to herbal remedies for simple ailments like coughs and colds. But today with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) the concept of home healthcare is getting a new definition. From the integration of smart healthcare devices to AI-powered tools, home healthcare is becoming more patient-centric, dynamic, and predictive.
Role of IoT in Home Healthcare
The home healthcare ecosystem is experiencing a massive transformation owing to the integration of IoT. The evolution of smart wearables and Bluetooth-connected health monitors are all gifts of IoT, making it easier to track one’s health status in the comfort of the home.
Today, diabetes patients can do more than just monitor their sugar levels. Bluetooth glucometers aid in logging the data automatically to the diabetes management app; thus, letting them track their sugar level patterns over time. It also enables easy data sharing with doctors, helping them make better decisions.
The acceptance and benefits of IoT in home healthcare can be well understood from the success story of CareNx. Its IoT-enabled kits for maternal care have helped millions of mothers with high-risk pregnancies in 6 countries and 20+ Indian states. The kit measures fetal heartbeat, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
Role of AI in Home Healthcare
AI analyses the data gathered by IoT devices using machine learning algorithms. This analysis aids in detecting even smaller changes taking place in a person’s health; allowing for early intervention.
In the larger context, the application of IoT and AI tools to large datasets can help to predict trends in the health of different populations with respect to ethnicity, age, gender, environmental factors and so on. Thus, it would lay the foundation for better healthcare studies while letting healthcare providers and policymakers make better and more evidence-based decisions.
Development of Equitable, Accessible and Affordable Healthcare System
In India, where nearly 70% of the population lives in rural regions; it has always been a challenge to provide them scalable and affordable health solutions. However, with telemedicine, smart wearables, and AI-powered diagnostic kits, it would be possible to break the geographical barriers.
For example, without even visiting hospitals, AI-powered chatbots allow patients to share their health queries. If a visit is required based on the discussions, then they are notified to do so. Thus, allowing urban healthcare to become a part of rural healthcare.
Owing to the IoT- and AI-driven transformation, remarkable improvements can be anticipated in the management of various health conditions in home healthcare settings. Numerous studies have shown that better health outcomes can be achieved with effective self-management, and these technologies are making that more achievable than ever.
For example, integration of IoT-enabled ECG can help to remotely monitor the heart health of patients. This allows real-time analysis and early detection of any subtle changes that could otherwise have had a deleterious consequence. It not only improves patient care but also reduces the need for hospital visits while empowering individuals to live more independently. Harvard’s School of Public Health has also accepted that using technologies like IoT and AI can help improve health outcomes by 40%.
Data Privacy and Security Challenges
Implementation of these technologies means more data generation; especially sensitive patient information. If any sort of breach occurs, then it could lead to consequences like identity theft or unauthorized insurance decisions. This raises questions about how well-protected the data is. Further, algorithmic bias in AI systems can result in discriminatory outcomes. The graveness of the situation further increases as technology often outpaces regulations, making adherence to strict regulations difficult.
Further, the high cost of this technology raises questions about its affordability; especially in low-resource settings. This will exacerbate the prevalence of digital divide and limit access for underserved populations. Another concern associated with technological implementation is that it may lead to over-reliance on technology. In turn, substituting human efforts and displacing jobs may further deteriorate the economic conditions of the people. Regarding patients, sole reliance on technology for analysis and interpretation of data can risk missing nuanced clinical judgments. So, it is vital to consider all these aspects so that an ethical implementation and usage of the technology can be achieved.
Final Thoughts
The future of healthcare does not lie in larger hospitals but in smarter homes. IoT–powered devices, AI-driven analysis, and human-centred design can create the foundation for safer, more accessible, and more intuitive home healthcare. This would be especially a blessing for a populous country like India. Thus, turning homes into healing hubs can change the overall scenario of the healthcare system.