Introduction
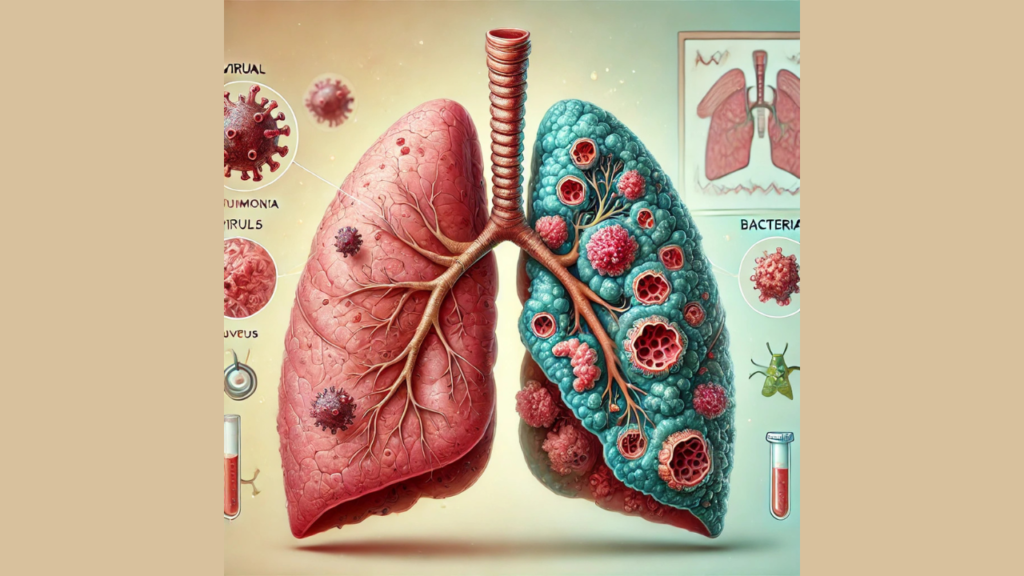
Pneumonia is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide each year. The infection can vary in severity, ranging from mild symptoms to life-threatening complications, depending on the type and how quickly it is treated. One of the most important distinctions in understanding pneumonia is knowing whether the infection is viral or bacterial. These two forms of pneumonia differ in their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between viral and bacterial pneumonia, discuss their respective symptoms, causes, and treatment methods, and highlight how you can prevent both types of pneumonia. By the end of this guide, you’ll be better equipped to understand the condition, seek appropriate care, and reduce the risks of complications.
What Is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs. The infection causes the alveoli to fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult and causing symptoms like cough, fever, chills, and shortness of breath. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, with bacterial and viral pneumonia being the most common.
Viral Pneumonia: Causes and Symptoms
Viral pneumonia is caused by a viral infection in the lungs. Several types of viruses can cause pneumonia, including:
- Influenza virus
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Adenovirus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Coronaviruses (including COVID-19)
Symptoms of Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia symptoms often mimic those of the common cold or flu, which can make it difficult to diagnose at first. However, the symptoms may worsen over time, leading to more severe respiratory issues. Common symptoms include:
- Dry cough
- Headache
- Fever (low-grade or high)
- Muscle aches and fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Sore throat
- Chest pain
- Chills
In some cases, viral pneumonia can progress rapidly and cause more serious issues such as respiratory failure, especially in older adults, infants, or those with weakened immune systems.
How Viral Pneumonia Spreads
Viral pneumonia spreads easily from person to person through airborne droplets when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks. People are more likely to catch viral pneumonia during cold and flu seasons.
Bacterial Pneumonia: Causes and Symptoms
Bacterial pneumonia is caused by bacteria entering the lungs and multiplying within the air sacs. One of the most common bacteria that causes bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other bacteria that may cause pneumonia include:
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Legionella pneumophila
Symptoms of Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia often develops quickly and can be more severe than viral pneumonia. Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia may include:
- High fever (often exceeding 101°F)
- Productive cough (producing greenish, yellow, or blood-streaked mucus)
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Confusion (especially in older adults)
- Sweating and shaking chills
- Bluish lips or nails due to lack of oxygen
While the onset of bacterial pneumonia is typically sudden, it can also develop after a viral infection, such as the flu, weakens the immune system and allows bacteria to grow in the lungs.
How Bacterial Pneumonia Spreads
Bacterial pneumonia is usually spread through close contact with an infected person, or by inhaling airborne bacteria. It can also develop when bacteria from another part of the body, such as the mouth or throat, spread to the lungs.
Key Differences Between Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia
There are several key differences between viral and bacterial pneumonia, including the severity of symptoms, progression of the illness, and how they are treated.
Onset and Severity
- Viral pneumonia tends to have a slower onset with milder symptoms that progressively worsen over time.
- Bacterial pneumonia has a rapid onset, often with high fever and severe respiratory symptoms, including a productive cough.
Fever and Cough
- Viral pneumonia often results in a low-grade fever and dry cough.
- Bacterial pneumonia is associated with a high fever and a productive cough that may produce yellow, green, or blood-tinged mucus.
Treatment
Treatment for viral and bacterial pneumonia differs significantly, and it’s important to get the correct diagnosis to receive the proper care.
Treatment Options for Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia does not respond to antibiotics, as these drugs are only effective against bacteria. Instead, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the body’s immune system as it fights off the infection. Common treatments include:
- Rest and plenty of fluids
- Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever and pain relief
- Antiviral medications (in cases of influenza-related pneumonia)
- Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Most people with viral pneumonia recover at home with supportive care, although hospitalization may be necessary in severe cases.
Treatment Options for Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia, on the other hand, can be effectively treated with antibiotics. Treatment may involve:
- Prescription antibiotics such as amoxicillin, azithromycin, or doxycycline
- Cough medications to help loosen mucus
- Plenty of rest and fluids
- Fever-reducing medications
For severe bacterial pneumonia, hospitalization may be required, where the patient may receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or respiratory support.
Complications of Pneumonia
Both viral and bacterial pneumonia can lead to serious complications, particularly in vulnerable groups such as infants, older adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems. Potential complications include:
- Respiratory failure: The lungs may not get enough oxygen into the bloodstream, requiring mechanical ventilation.
- Sepsis: Infection can spread to the bloodstream and affect other organs.
- Lung abscess: Pockets of pus may form in the lungs, requiring surgical drainage.
Prevention of Pneumonia
Taking steps to prevent pneumonia is crucial, especially for those at higher risk. Prevention strategies include:
- Vaccination: Pneumonia vaccines like the pneumococcal vaccine and the flu vaccine can help reduce the risk.
- Hand hygiene: Washing hands regularly helps prevent the spread of infections.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can strengthen the immune system.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between viral and bacterial pneumonia is crucial for proper treatment and prevention. While both types of pneumonia can be serious, bacterial pneumonia typically requires antibiotics, whereas viral pneumonia is managed with supportive care. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for a full recovery.
To prevent pneumonia, make sure to stay up to date on vaccinations, maintain good hygiene, and adopt a healthy lifestyle. By taking these steps, you can reduce your risk and keep your lungs healthy.