Introduction
Athletes are always seeking ways to enhance their performance and prevent injuries. While traditional training methods are essential, incorporating yoga into an athlete’s routine can be transformative. This ancient practice not only improves flexibility and strength but also promotes mental clarity, focus, and recovery. In this blog, we will explore how yoga can enhance athletic performance, reduce the risk of injuries, and provide athletes with the tools they need to excel in their sport.
The Benefits of Yoga for Athletes
1. Improved Flexibility
Flexibility is crucial for athletes in nearly every sport. Increased flexibility can lead to better performance and a reduced risk of injuries. Yoga poses stretch and lengthen muscles, improving the range of motion in joints. For example, athletes who engage in sports that require explosive movements, such as sprinting or jumping, can greatly benefit from the flexibility gained through yoga.
2. Enhanced Strength
While yoga may not seem like a traditional strength-training method, many yoga poses require significant strength and engage multiple muscle groups. For instance, poses like Warrior II and Plank help build core strength, which is essential for stability in almost every sport. Increased strength gained through yoga can lead to improved performance and better overall endurance.
3. Improved Balance and Coordination
Yoga emphasizes balance and stability, which are essential for athletes. Poses such as Tree Pose and Eagle Pose challenge the body’s balance and coordination, helping athletes develop better control over their movements. This enhanced coordination can lead to better performance in sports that require agility and precision, such as gymnastics or martial arts.
4. Increased Body Awareness
Yoga promotes mindfulness and body awareness, allowing athletes to connect with their bodies on a deeper level. This awareness helps athletes identify muscle imbalances and areas of tightness, enabling them to address these issues proactively. Improved body awareness can lead to better technique and performance, as athletes become more in tune with their movements.
5. Mental Clarity and Focus
The mental aspect of athletic performance is often overlooked, but it is just as important as physical training. Yoga incorporates breathing techniques and meditation that enhance mental clarity and focus. Athletes who practice yoga report improved concentration and reduced anxiety, allowing them to perform better under pressure. Techniques such as Pranayama (breath control) can help athletes manage stress and anxiety during competitions.
Yoga Poses for Athletes
Incorporating specific yoga poses into an athlete’s routine can target the muscle groups most commonly used in their sport. Here are some effective yoga poses for athletes:
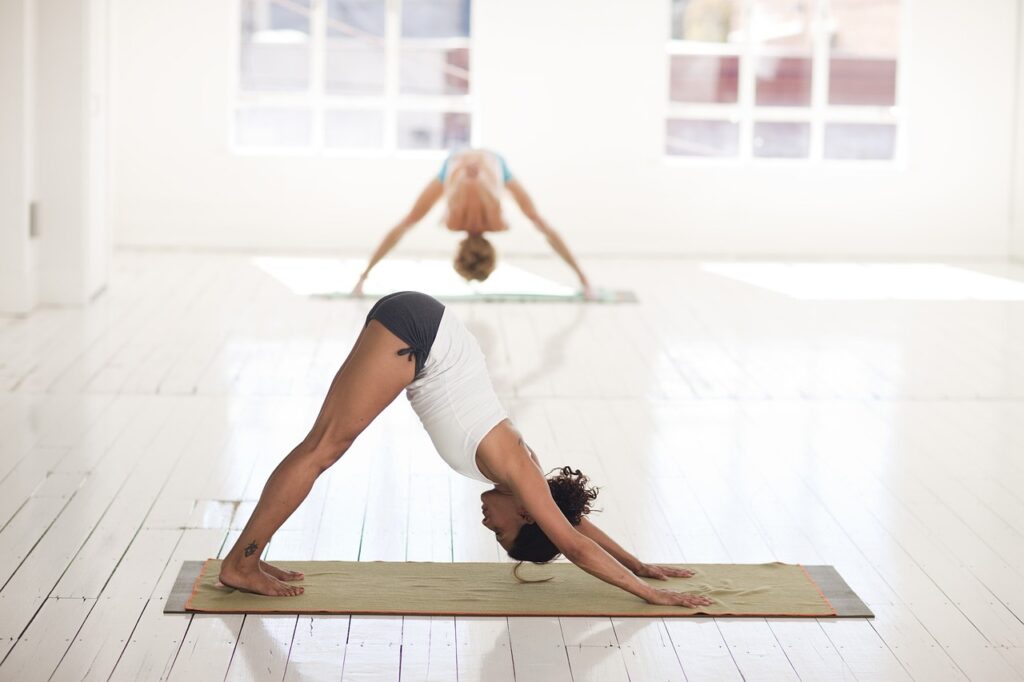
1. Downward-Facing Dog (Adho Mukha Svanasana)
The entire body is stretched in this pose, but the shoulders, calves, and hamstrings are especially worked. It also helps relieve tension in the spine, making it a great pose for recovery.
2. Pigeon Pose (Eka Pada Rajakapotasana)
Pigeon Pose is excellent for opening the hips, which can become tight from running or cycling. This pose helps improve hip mobility and relieve lower back pain.
3. Warrior II (Virabhadrasana II)
Warrior II is a strong pose that enhances balance and concentration while strengthening the legs and core. It is particularly beneficial for athletes in sports that require strong lower body strength.
4. Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana)
Bridge Pose helps strengthen the glutes, lower back, and hamstrings. It also opens up the chest and shoulders, promoting better posture, which is vital for athletes.
5. Child’s Pose (Balasana)
This restorative pose is great for relaxation and recovery. It helps stretch the hips, thighs, and lower back, making it ideal for athletes after an intense workout.
Yoga for Injury Prevention
Injuries can be a significant setback for athletes. Yoga helps prevent injuries in several ways:
1. Addressing Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances are a common side effect of repetitive activities in sports. Yoga helps correct these imbalances by promoting balanced strength and flexibility throughout the body.
2. Enhancing Recovery
Yoga promotes relaxation and recovery by increasing blood flow to the muscles. Regular practice can reduce muscle soreness and stiffness, allowing athletes to bounce back faster after intense training sessions.
3. Reducing Stress
Stress can lead to muscle tension and hinder performance. Yoga provides athletes with the tools to manage stress effectively, reducing the likelihood of injuries caused by physical and mental strain.
Integrating Yoga into Your Training Routine
1. Start Slow
For athletes new to yoga, it’s essential to start slowly. Begin with a few classes each week, focusing on foundational poses and breathing techniques.As you get more accustomed to the practice, gradually up the frequency and intensity.
2. Consider Your Sport
Choose yoga classes or poses that align with your specific sport. For example, runners may benefit from poses that focus on hip flexibility, while swimmers may need to emphasize shoulder mobility.
3. Combine with Traditional Training
Yoga should complement, not replace, traditional training methods. Incorporate yoga sessions into your weekly routine to enhance your overall performance while still engaging in sport-specific training.
4. Find a Qualified Instructor
Consider taking classes from a qualified yoga instructor who has experience working with athletes. They can provide guidance on proper alignment and help you tailor your practice to meet your specific needs.
Conclusion
Yoga is a powerful tool for athletes looking to enhance their performance and prevent injuries. By improving flexibility, strength, balance, and mental focus, yoga can provide a competitive edge. Additionally, its role in injury prevention and recovery makes it an essential component of any athlete’s training regimen. Whether you are a seasoned athlete or just starting, integrating yoga into your routine can lead to improved performance, increased body awareness, and a more balanced approach to training.